Case StudyAtlantic Racquet Centre Case Study – Powervault and GMEC
Introduction
The Atlantic Racquet Centre (ARC) is a new community racquets and fitness centre in Bideford, North Devon, where everyone can exercise, socialise and learn together. The centre is a volunteer led community business and charity focused on improving the health and wellbeing of all local people.
The ARC team were determined to make the centre have as low a carbon footprint as possible and so everything is powered by electricity – LED lighting for the courts, air source heat pump for the heating and hot water, electric cooking facilities. They then approached Powervault, the UK’s leading manufacturer of smart home energy storage systems, for advice on how to minimise the cost and carbon intensity of this electrical demand. Working in partnership with local solar and storage specialists GMEC, Powervault came up with a solution.
Solution
Based on the forecast electricity demand from all this equipment and the fact that the busiest time for ARC is in the evenings, the combination of 60kW of solar PV and 60kWh battery storage was agreed. The installation was completed by GMEC in July 2021 and the immediate reduction in electricity imported from the grid was pretty impressive. In the first month since installation, 80% of the site’s energy consumption has been met by the solar PV/Powervault combination, i.e. by 100% renewable energy generated on site. This has either been consumed directly from the solar PV during the day, or in the evening after being stored in the Powervault batteries.
On sunny days, the energy generated from the solar panels is first used to meet the electricity demand on site at that particular time. If there is a surplus, that surplus is stored in the Powervaults until the Powervaults are full so that energy can be used later in the evening once the sun has gone down. If there is still a surplus generated, that will be diverted to heat the hot water via a smart hot water controller called an Eddi made by another UK company, My Energi, and also installed by GMEC. Only then will any surplus solar PV be exported to the grid to be used elsewhere.

Results
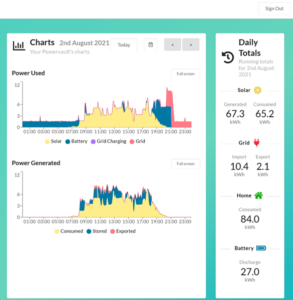
Powervault portal for phase 1 on 2/8/2021 showing 88% of demand met by solar PV, direct (yellow) or via storage (blue)
Powervault portal for phase 1 on 2/8/2021 showing 88% of demand met by solar PV, direct (yellow) or via storage (blue)
In the evenings on site electricity demand is first met by what is stored in the Powervaults and only imported from the grid once this has been exhausted.
The next step for ARC is to sign up to a Time of Use tariff from a green energy supplier. This will mean that in the winter when there is not much sun, the Powervaults can be charged up using cheaper overnight low carbon electricity from the grid.
The data available from the Powervault portal showing the actual energy consumption on each of the 3 phases means that ARC can gain a deep understanding of their usage and make sensible decisions about what is turned on when to help minimise their energy costs.
“This project is a great example of how intelligent use of new technology can be combined to help create a state-of-the-art leisure facility with both low carbon footprint and low energy costs.”
Anoushka Lynd, chair of the ARC board,
Read more...Recent Case studies
Energy insight in your inbox
Subscribe to Powervault’s email newsletter and be the first to hear about new products, plus get all the latest news, analysis and insight from Powervault.


